Wake-on-LAN
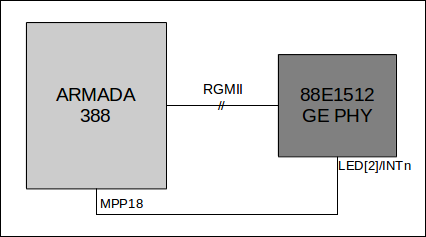
The Armada 388 SoC provides several trigger options from different peripherals to wake up the system out of power save modes. Some of the options are:
- Wake on GPIO
- Wake on LAN
Currently Helios4 uses the PHY interrupt and 'Wake on GPIO' event to implement Wake-on-LAN.
Add WoL Support¶
Note
Starting Armbian version 5.77 the Wake-on-LAN support has been added by default. So you might want to upgrade your system via APT to skip this section.
Device Tree¶
Linux provides gpio-keys driver to handle GPIO event and can be configured as wakeup source.
gpio-keys {
compatible = "gpio-keys";
pinctrl-0 = <µsom_phy0_int_pins>;
wol {
label = "Wake-On-LAN";
linux,code = <KEY_WAKEUP>;
gpios = <&gpio0 18 GPIO_ACTIVE_LOW>;
wakeup-source;
};
};
Device Tree Patch can be found here.
Kernel¶
Current gpio-mvebu driver does not implement irq_set_wake() to support GPIO as wakeup source and properly route it to upper interrupt controller (Arm GIC).
This will raise following issues:
- System unable to wake up from Suspend-to-RAM
- System wake up from GPIO interrupts not defined as wakeup source
- Kernel crash during wakeup from standby
[ 59.169436] ------------[ cut here ]------------
[ 59.174075] WARNING: CPU: 0 PID: 1535 at kernel/irq/manage.c:623 irq_set_irq_wake+0xe4/0x11c
[ 59.182533] Unbalanced IRQ 50 wake disable
[ 59.186638] Modules linked in: lz4hc lz4hc_compress marvell_cesa zram zsmalloc lm75 pwm_fan ip_tables x_tables
[ 59.196690] CPU: 0 PID: 1535 Comm: bash Not tainted 4.14.94-mvebu+ #14
[ 59.203234] Hardware name: Marvell Armada 380/385 (Device Tree)
[ 59.209183] [<c01118d0>] (unwind_backtrace) from [<c010c7cc>] (show_stack+0x10/0x14)
[ 59.216955] [<c010c7cc>] (show_stack) from [<c095091c>] (dump_stack+0x88/0x9c)
[ 59.224204] [<c095091c>] (dump_stack) from [<c012ab9c>] (__warn+0xe8/0x100)
[ 59.231188] [<c012ab9c>] (__warn) from [<c012abfc>] (warn_slowpath_fmt+0x48/0x6c)
[ 59.238696] [<c012abfc>] (warn_slowpath_fmt) from [<c017bb64>] (irq_set_irq_wake+0xe4/0x11c)
[ 59.247160] [<c017bb64>] (irq_set_irq_wake) from [<c0747594>] (gpio_keys_resume+0xb0/0x11c)
[ 59.255537] [<c0747594>] (gpio_keys_resume) from [<c0654b34>] (dpm_run_callback+0x54/0xec)
[ 59.263826] [<c0654b34>] (dpm_run_callback) from [<c0655180>] (device_resume+0xcc/0x270)
[ 59.271941] [<c0655180>] (device_resume) from [<c0656660>] (dpm_resume+0x100/0x230)
[ 59.279621] [<c0656660>] (dpm_resume) from [<c06569e4>] (dpm_resume_end+0xc/0x18)
[ 59.287128] [<c06569e4>] (dpm_resume_end) from [<c0175af8>] (suspend_devices_and_enter+0x210/0x5e0)
[ 59.296202] [<c0175af8>] (suspend_devices_and_enter) from [<c01761c0>] (pm_suspend+0x2f8/0x380)
[ 59.304927] [<c01761c0>] (pm_suspend) from [<c0174a30>] (state_store+0x70/0xcc)
[ 59.312260] [<c0174a30>] (state_store) from [<c02c80e4>] (kernfs_fop_write+0xe8/0x1c4)
[ 59.320204] [<c02c80e4>] (kernfs_fop_write) from [<c024ce78>] (vfs_write+0xa4/0x1b4)
[ 59.327972] [<c024ce78>] (vfs_write) from [<c024d0b4>] (SyS_write+0x4c/0xac)
[ 59.335045] [<c024d0b4>] (SyS_write) from [<c0108620>] (ret_fast_syscall+0x0/0x54)
[ 59.342633] ---[ end trace c725de247edb5ce9 ]---
[ 59.474369] ata2: SATA link down (SStatus 0 SControl 300)
[ 59.474443] ata3: SATA link down (SStatus 0 SControl 300)
[ 59.638619] ata1: SATA link down (SStatus 0 SControl 300)
[ 59.647170] ata4: SATA link up 3.0 Gbps (SStatus 123 SControl 300)
[ 60.081905] ata1: SATA link down (SStatus 0 SControl 300)
[ 60.087343] ata1: limiting SATA link speed to 1.5 Gbps
[ 60.386518] mvneta f1070000.ethernet eth0: Link is Down
[ 60.578411] ata1: SATA link up 1.5 Gbps (SStatus 113 SControl 310)
[ 61.162892] ata4.00: configured for UDMA/100
[ 62.431232] mvneta f1070000.ethernet eth0: Link is Up - 1Gbps/Full - flow control rx/tx
[ 63.087435] ata1.00: configured for UDMA/100
[ 63.159889] OOM killer enabled.
[ 63.164643] Restarting tasks ... done.
[ 63.181059] PM: suspend exit
To fix the issue, gpio-mvebu driver needs to be patched to implement irq_set_wake() and only enable interrupt on GPIO defined as wakeup source.
Patch for Linux Kernel 4.14.x can be found here
Enabling WOL¶
Note
Latest Armbian images, starting version 5.77, should already have the WoL enabled by default for eth0. Check that file /lib/systemd/system/helios4-wol.service exist and match the configuration file below.
Enable the PHY to raise an interrupt when magic packet received :
sudo ethtool -s eth0 wol g
To make it permanent, create the following file /lib/systemd/system/helios4-wol.service and copy the following:
[Unit]
Description=Enable Wake-on-LAN for Helios4 eth0
After=network-online.target
Wants=network-online.target
[Service]
ExecStart=/sbin/ethtool -s eth0 wol g
Type=oneshot
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
Then reload systemd manager configuration
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
Suspend System¶
Use systemctl command to put your system in suspend mode.
sudo systemctl suspend
Important
Only execute this command after enabling WOL otherwise there is a risk that Helios4 will not wake up when receiving magic packet. More explanation regarding this issue on here.
Wake up System¶
To wake up your suspended Helios4 you need to send it a magic packet from a machine on the same network.
Before putting Helios4 in suspend mode, you need to know its MAC address. Use ip link command. In the example below the MAC address is 02:fc:e7:3d:b8:c8.
ip link
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
2: eth0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc mq state UP mode DEFAULT group default qlen 532
link/ether 02:fc:e7:3d:b8:c8 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
3: tunl0@NONE: <NOARP> mtu 1480 qdisc noop state DOWN mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/ipip 0.0.0.0 brd 0.0.0.0
From a Linux machine (running Debian/Ubuntu) on the same network :
- Install etherwake tool
sudo apt-get install etherwake
- Send magic packet
sudo etherwake 02:fc:e7:3d:b8:c8
If your system doesn't have an interface named eth0, you will need to specify the network interface you want to use to send out the magic packet. Example :
sudo etherwake -i enx00051bd1ca66 02:fc:e7:3d:b8:c8
You can refer to this guide from cyberciti.biz.
Power Consumption¶
Measured using Sonoff POW R2 on AC side
| Power state | Power (Watt) | Current (Ampere) | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Idle | 19.87 | 0.17 | |
| Standby | 8.63 | 0.10 | HDD in Standby mode |
| Suspend | 7.71 | 0.08 | HDD in Standby mode |
Note
- Nominal Input Voltage: 220V
- HDD: 4x WD Red 2TB (WD20EFRX)
- I2C OLED screen attached to the systems
Issues¶
Unexpected Packet¶
The PHY INT pin is supposed to be handled by the Ethernet controller so when there is an interrupt the driver can respond and acknowledge the interrupt. Without this acknowledgment, the PHY INT pin will stay active and the PHY won't trigger another interrupt.
On specific case that after user enabled the WOL and magic packet received before entering suspend mode, Helios4 will not able to wake up. The reason is PHY interrupt already triggered before entering suspend mode and no other interrupt triggered during suspend mode. The Ethernet controller driver will reset PHY interrupt during resume and when enabling WOL.
Therefore it is advised to always enable WOL (sudo ethtool -s eth0 wol g) before entering suspend.
Thermal¶
When system is put in suspend mode, the PWM feature controlling the fan speed is stopped. The fans will either spin at their lowest speed (Batch 1 & 3 fan) or stop spinning (Batch 2 fan). In the latest case, while it is not an issue for the SoC itself which is designed to run with passive cooling, it might have a negative impact on the HDD peripherals because the ambient temperature inside the case will rise.
Therefore it is advised to ensure that when system is suspended the case ambient temperature will not exceed the operating temperature your HDDs are rated for.